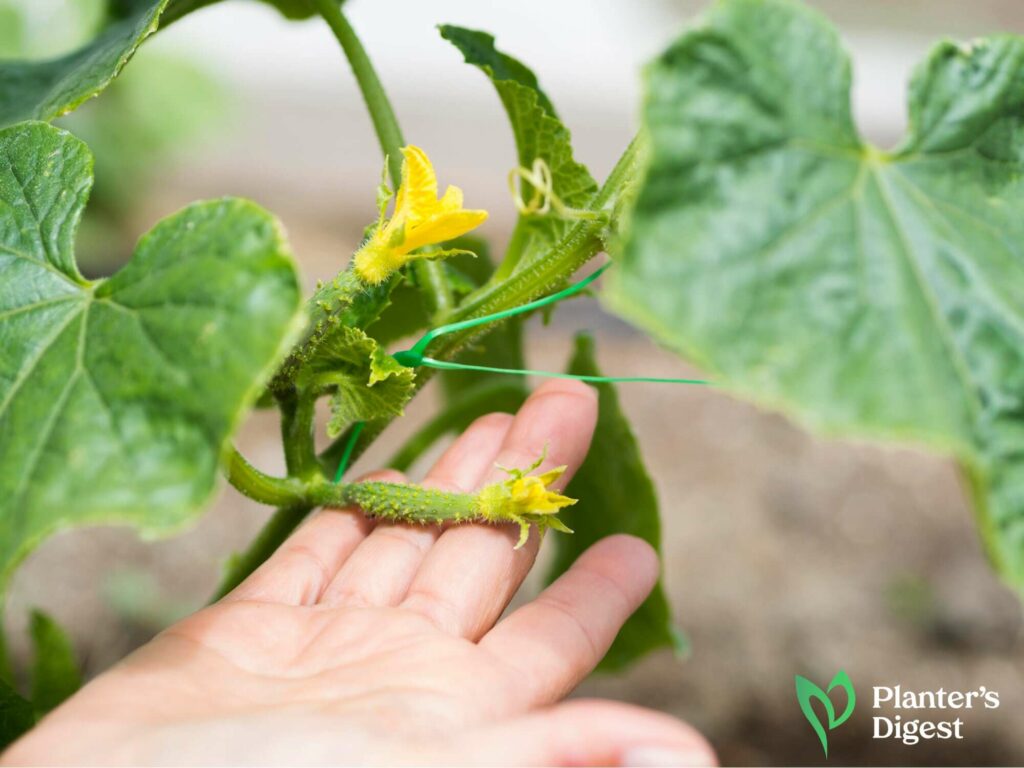
Pollination is a crucial step in a plant’s life. It’s like the bridge toward fulfilling its destiny – to produce those delicious fruits that we all love.
But every plant has a different way of being pollinated. Pepper plants are self-pollinating, which means they can pollinate themselves as long as the female part of the flower receives the pollen and produce peppers on their own.
Let’s take a closer look at pepper plant pollination in this article!
Do peppers need to be pollinated?

Peppers need to be pollinated to produce fruit. They are self-pollinating, but animals and other plants can also help pollinate pepper plants.
Pepper flowers have both male and female parts. During pollination, the male part of the flower releases pollen, while the female part receives the pollen.
Once a pepper flower is pollinated, it will start to produce fruit.
Factors that Prevent Pepper Plants from Self-Pollinating

Pepper plant flowers will not self-pollinate if the temperature is too high, too low, humid or there are no pollinators around.
Read on to learn how each of these factors prevents pollination of pepper plants.
1. Extreme Temperature

Pepper plants need a specific temperature range to grow and produce fruit. The plants will not pollinate or set fruit if the temperature is too cold or hot.
At night, pepper plants need temperatures above 58 °F for pollination and for their fruit to set. During the daytime, pepper plants need temperatures below 90 °F for pollination and fruit set.
Otherwise, the pepper plant will not be able to pollinate, and its flowers will drop.
2. Extreme Humidity
Humidity is another crucial factor in pollinating pepper plants. Too little or too much humidity will spell doom for your pepper plants.
If the air is excessively humid, pollen may become sticky and fail to detach from the male part of the flower.
Conversely, if the air is excessively dry, pollen may not be sticky enough to stick to the female part of the flower.
If you have a greenhouse, it’s important to air it regularly to prevent the humidity level from getting too high. Since no wind or fewer animal pollinators can enter your greenhouse, maintaining the humidity level will encourage your pepper plants to just self-pollinate and produce fruit.
4. Lack of Wind
Pepper plants need wind to help their flowers pollinate. The breeze of the wind shakes the pollen off the flowers and towards to female part of the plant.
If you’re growing your pepper plants in a greenhouse, you can simulate the wind by focusing a fan on the flowers of your plant or briefly bringing them outside each day.
5. Lack of Pollinators
Many animals are declining in number and are close to extinction. Unfortunately, bees are also one of those species with alarmingly declining numbers in some parts of the world.
Besides using pesticides that harm these pollinations, extreme heat or cold can also stop bees from pollinating flowers.
So, to encourage animal pollination, you’ll also have to keep your garden safe and attractive for these insects. Some plants that attract pollinators include lavender, aster, sunflower, coneflower, marigold and cosmos.
Methods of Pollination for Pepper Plants
There are three ways to pollinate a pepper plant: self-pollination, animal pollination, hand pollination and cross-pollination.
Let’s discuss each method and how to apply them to your pepper plant.
1. Animal Pollinators
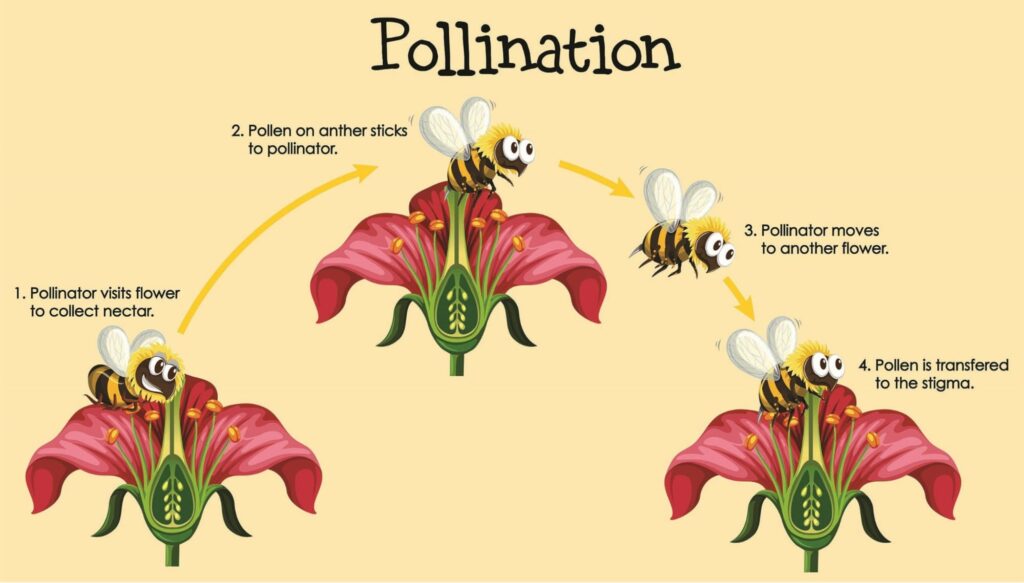
Pollinators are amazing creatures that help to pollinate pepper flowers. They’re crucial for peppers and various plants so we would have more food with pollinators!
As a gardener, pollinators are your best friend. They can help your plants produce a more significant yield and even assist with developing fruits that might not have been possible otherwise.
To help attract pollinators, you can plant more flowers in your garden and avoid using pesticides that harm them.
2. Hand Pollination
Hand pollination is a great way to ensure that your pepper plants produce fruit. All you need to do is gently rub the flower’s male parts against the female parts.
As you perform hand pollination, remember that the male part is easily identifiable by the pollen sacs at the tip of its stamen, while the female part has a sticky stigma at its center.
This will transfer the pollen from the anthers to the stigma, fertilizing the flower and eventually producing peppers for you to enjoy.
The good news is that hand pollination can lead to a 100% fruit set, meaning all the flowers on your pepper plant will produce fruit. It can also help to produce larger peppers with more seeds.
Using your hand or tool, you must gently rub the male flower’s anthers against the female flower’s stigma. Repeat this process with as many flowers as you like, and water your pepper plants well afterward.
How to Hand-Pollinate Peppers
Here are ways to hand-pollinate your pepper plant using a paintbrush, toothbrush, toothpick or shaking them.
1. Use the bristles of a brush to release pollen.

| Difficulty | Easy ●○○○○ |
| Duration | 10 to 15 minutes |
| Things You Need | Paintbrush or bristle brush |
You can pick up a bristle bush to get closer and deeper and scoop the pollens in the flower. This way, pollens will cling to the natural bristles, and you’ll release more pollen to the female part of the pepper flower.
Make sure to clean the paintbrush to prevent the spread of plant diseases or cross-pollination.
How To Do
Pull up the flowers of the pepper plant. Wipe the brush on the inside of the flower. Twirl the brush to collect as much pollen as you can. Rub the brush on the tip of the center of the flower.
2. Use a battery-operated toothbrush to release the pollen.
| Difficulty | Easy ●○○○○ |
| Duration | 10 to 15 minutes |
| Things You Need | Battery-operated toothbrush |
You can also use a battery-operated toothbrush to hand-pollinate a pepper plant. This is a way to replicate the movement of the bees’ wings, where their anthers encourage the release of pollen and drop them onto the stigma of the pepper flowers.
How To Do
Place the vibrating toothbrush on the flower’s base or stem until the pollen falls off. Drop the pollen onto the tip of the center of the flower.
3. Use a toothpick to shake the pollen off the flower.
| Difficulty | Easy ●○○○○ |
| Duration | 10 to 15 minutes |
| Things You Need | Toothpick |
Using a toothpick is an easy and budget-friendly way to hand-pollinate a pepper plant. All you have to do is to brush this thin wood to gather pollen and release it on the female part of the pepper flower.
How To Do
1. Gently push up or down on the flower to move it out of place.
2. Let go of the toothpick, and the flower will move back into place.
3. The movement and vibration will cause the male part of the flower to release its pollen.
4. Repeat this process with as many flowers as you like.
4. Shake the flower.
| Difficulty | Easy ●○○○○ |
| Duration | 10 to 15 minutes |
| Things You Need | Just yourself. |
It’s hard to pollinate pepper plants when there’s no wind. So, why not mimic the wind breeze by gently shaking your pepper plant?
As you shake the pepper stems, you’re mimicking the motion of the wind to release the pollen from the plant. In a few seconds, loose pollen will drop to the center of the flower, and your plant will produce peppers in no time.
How To Do
1. Flick the stems close to the base of the flower of the pepper plant.
2. Tap the end of the flowers.
How long after pollination do peppers appear?
After pollination, it takes 45 to 55 days for the pepper to mature to full size. At this point, it will produce deep, dark green peppers ready for ripening.
Usually, you’ll see a puff of yellow pollen emerge from the flower after hand pollination, which is a sign of its success. Eventually, a fruit will start to form where the flower was, and the pepper fruit will appear behind it.
It takes another 15 days for the pepper to turn deep red. So, you are looking at 60 to 70 days from flower pollination to mature red bell peppers ready for harvest.
FAQs on Pepper and Self-Pollination
Peppers cannot be planted in pairs because they can reproduce independently via self-pollination. However, planting them in pairs can help them cross-pollinate and produce more fruit.
A pepper flower is pollinated when it produces a small white seed pod at the base of the flower.
One pepper plant can produce 6 to 8 peppers, but some varieties with smaller peppers can yield more than ten peppers per plant.
Peppers can be pollinated by transferring the pollen from one plant to another. As a result, a hybrid pepper variety is produced by both pepper plants.
The chili plant is a cross-pollinated crop and is commonly visited by insects carrying pollen from other pepper varieties.
Peppers do not necessarily need to be pollinated by bees to produce fruits. They are already perfect flowers with both the anther and the stigma to self-fertilize.





